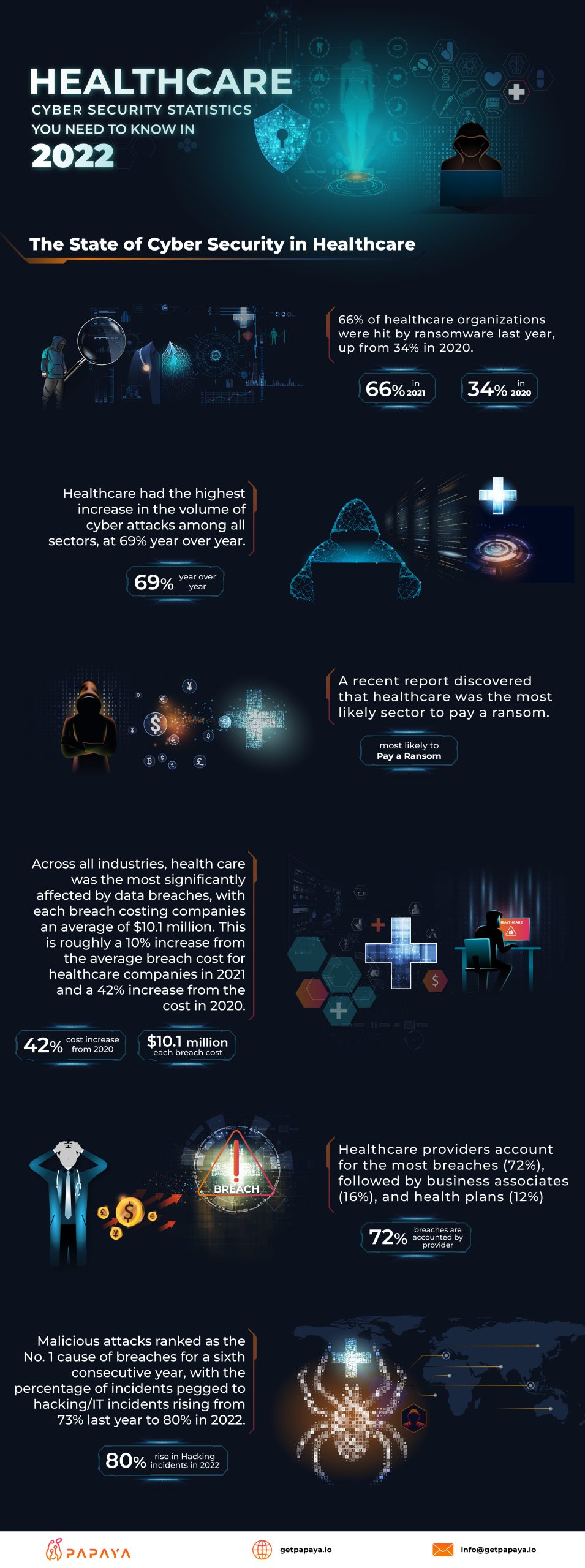
The State of Cybersecurity in Healthcare
The healthcare industry has been hit hard by cyber attacks in recent years, with the number of healthcare organizations affected by ransomware growing from 34% in 2020 to 66% in 2021. This represents the highest increase in cyber attack volume among all sectors, with a 69% year-over-year increase.
A recent report on the state of cyber security in the healthcare industry revealed that healthcare providers are the most likely sector to pay a ransom in the event of a cyber attack. This is likely due to the sensitive nature of healthcare data and the potential consequences of not paying a ransom, such as a disruption in patient care. The cost of data breaches in the healthcare industry is also significant, with each breach costing companies an average of $10.1 million. This represents a 10% increase from the average cost of a breach in 2021 and a 42% increase from the cost in 2020.
Healthcare providers account for the majority of breaches in the industry, with 72% of incidents occurring at these organizations. Business associates, such as third-party vendors and suppliers, account for 16% of breaches, while health plans account for the remaining 12%.
Malicious attacks, such as hacking and IT incidents, continue to be the leading cause of data breaches in the healthcare industry. In 2021, these types of incidents accounted for 80% of all breaches, up from 73% in 2020. This trend is expected to continue in 2022 as cyber criminals become more sophisticated and healthcare organizations struggle to keep pace with the evolving threat landscape.
It is imperative for healthcare organizations to take proactive measures to protect their systems and data from cyber attacks. This includes implementing robust security protocols, regularly updating software and systems, and educating employees on how to identify and prevent potential threats. By taking these steps, healthcare organizations can reduce the risk of a data breach and minimize the potential costs associated with a cyber attack.




